What is Schedule 40 and Schedule 80?
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 are terms used to classify the wall thickness of pipes, influencing their strength and pressure-handling capacity. These classifications are part of standards set by ANSI (American National Standards Institute) to ensure pipes are suitable for specific applications.
- Schedule 40 Pipes: Known for their thinner walls, they are lightweight and primarily used in low-pressure systems like residential plumbing, irrigation, and drainage.
- Schedule 80 Pipes: These thicker walls offer higher strength and durability, making them ideal for high-pressure and industrial systems.
Both schedules are available in materials such as PVC, steel, and CPVC, and selection depends on factors such as pressure requirements, material compatibility, and application type.
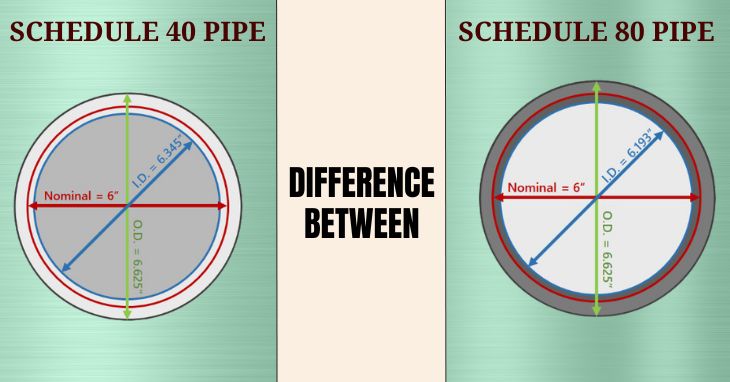
Difference Between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 Pipes
Wall Thickness:
Schedule 40 pipes have thinner walls, making them suitable for lighter applications like residential and landscaping projects. Schedule 80 pipes, on the other hand, have thicker walls, providing additional strength for systems that need to handle higher pressures.
Pressure Capacity:
Schedule 40 pipes are designed for low-pressure tasks, such as water transport and irrigation systems. In contrast, Schedule 80 pipes are built to manage high-pressure requirements, making them ideal for industries like oil, gas, and chemicals, where durability is critical.
Weight and Cost:
Because of their thinner walls, Schedule 40 pipes are lighter and more cost-effective. Schedule 80 pipes are heavier and more expensive due to the additional material required for their construction.
Applications:
Schedule 40 is widely used for residential plumbing, landscaping, and light-duty systems. Schedule 80 is preferred for industrial piping, chemical transport, and systems that demand higher pressure tolerance.
What are the Specification Standards for Them?
Regulatory Bodies: Standards are set by ANSI, ASTM, and ASME to ensure uniform quality and performance.
Outer Diameter (OD): For a given nominal pipe size, both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes share the same OD.
Wall Density: Schedule 80 pipes have thicker walls than Schedule 40, providing greater strength.
Pressure Ratings: Higher for Schedule 80 pipes due to the added material and increased durability.
Materials: Common materials include PVC (ASTM D1785), CPVC, and steel (ASTM A53), chosen based on application requirements.
Conclusion
Choosing between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 pipes depends on your project’s requirements. Schedule 40 is cost-effective and ideal for low-pressure systems like household plumbing. In contrast, Schedule 80 is better suited for high-pressure or industrial applications where strength and durability are essential. Selecting the appropriate schedule ensures any piping system’s safety, reliability, and cost-efficiency.